For emergency veterinarians, interns and residents, ECC and anesthesia technicians seeking to truly master emergency and critical care topics, traditional continuing education (CE) courses, webinars, and lectures may prove to be inadequate. These conventional methods often fall short in several key aspects, hindering effective learning and retention. Over the last 15 years, I have attended dozens of CE events and watched hundreds of hours of webinars, only to realize a week later that I can recall 5-10% of this information. Have you ever felt that way?
Continue reading “From Novice to Expert: How to Master Small Animal Electrolyte and Acid-Base Disorders?”Blog
Traumatic Brain Injury in a Cat: Hyperglycemia and suspected central diabetes insipidus
“Eyeballing” Left Ventricular Function in Dogs and Cats Presenting in Shock
In emergency situations, particularly when treating pets in shock, quickly assessing left ventricular (LV) function is crucial for determining the best course of action and accurately diagnosing the type of shock (cardiogenic vs. hypovolemic vs. distributive vs. obstructive). A fast, reliable method that emergency veterinarians can use is Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS). This “eyeball” approach allows us to evaluate LV contractility efficiently.
In this post, I’ll walk you through the three primary components of LV function assessment using POCUS, which can be easily applied by non-cardiologists. By mastering these techniques, you’ll be able to identify whether your patient’s LV function is hyperdynamic, normal, or depressed in just a few moments.
Continue reading ““Eyeballing” Left Ventricular Function in Dogs and Cats Presenting in Shock”Can Venous Blood Be a Substitute for Arterial Samples during CPR?
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) can be a chaotic event, requiring rapid decisions and careful management of both basic and advanced life support. Among the tools used to assess patient status during resuscitation is point-of-care blood gas analysis. But one question arises: Is there a clinical advantage to using arterial blood over venous blood during CPR, or can venous samples provide equally useful information?
In a recent study, researchers explored this exact question, looking at blood gas values in dogs undergoing CPR to see whether venous blood might stand in for arterial blood in critical situations. Let’s dive into what they found and what it means for veterinary practice.
Continue reading “Can Venous Blood Be a Substitute for Arterial Samples during CPR?”A Tricky Enterococcus
A 7-year-old spayed female Persian cat was presented to an emergency service for evaluation of fever, chronic vomiting, and severe lethargy. On initial examination, the cat was stuporous, with fair femoral pulses, pale pink mucous membranes, moderate dehydration, a body temperature of 104°F (40°C), and a heart rate of 150 beats per minute. The initial work-up suggested septic peritonitis and partial jejunal mechanical obstruction, based on abdominal ultrasound and abdominal fluid cytology. Stabilization included fluid resuscitation and intravenous antibiotics (ampicillin/sulbactam at 30 mg/kg IV q8h and enrofloxacin at 5 mg/kg IV q24h), followed by norepinephrine (0.1 mcg/kg/min) due to persistent arterial hypotension. Three hours after presentation, the cat underwent exploratory laparotomy, which revealed a foreign body in the jejunum causing obstruction and perforation. Post-lavage peritoneal swabs were submitted for culture and sensitivity. The cat received resection and anastomosis, along with JP drain placement. Norepinephrine was discontinued 36 hours post-surgery, and nasogastric tube feeding was initiated shortly thereafter.
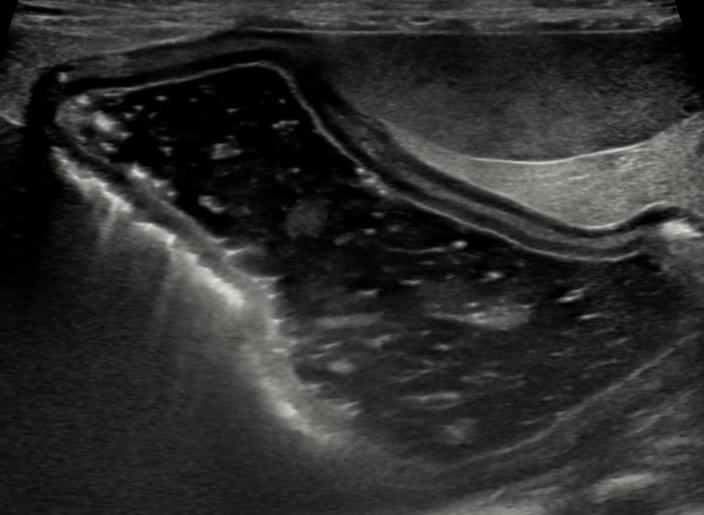
Gas in the gastric wall: The Good and the Bad
A 15 year-old neutered male Chihuahua was presented to a university teaching hospital for further evaluation of acute vomiting, anorexia, hyperbilirubinemia and elevated liver enzymes. The abdominal ultrasound was suggestive of acute severe pancreatitis resulting in extrabiliary bile duct obstruction. In addition, the gastric wall contained intramural gas consistent with gastric pneumatosis (Figure 1).
Continue reading “Gas in the gastric wall: The Good and the Bad”